Anti-IL-6 antibody clazakizumab in late antibody-mediated rejection – Molecular rebound phenomena under IL-6 blockade?
Anita Borski1, Susanne Haindl2, Michael Dürr3, Klemens Budde3, Sabine Schranz1, Farsad A. Eskandary2, Konstantin Doberer2, Philip F. Halloran4, Edward Chong5, Bernd Jilma1, Georg A. Böhmig2, Markus Wahrmann2.
1Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria; 2Department of Medicine III, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria; 3Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care , Charité University Medicine Berlin, Berlin, Germany; 4Department of Medicine, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada; 5Vitaeris Inc., Vancouver, BC, Canada
Introduction: Late antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) is well established as a major cause of kidney allograft failure. Targeting interleukin-6 (IL-6), a pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in B cell activation and development may represent a promising therapeutic strategy. One may argue that the effects of prolonged blockade of the IL-6/IL-6 receptor axis may be overcome by rebound phenomena, as earlier described for anti-IL-6R monoclonal antibodies, which lead to a profound accumulation of serum IL-6. In quest of a similar effect of anti-IL-6 treatment, we monitored biological samples from an ongoing bi-center, randomized controlled phase 2 pilot trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of anti-IL-6 antibody clazakizumab in late ABMR (www.clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03444103).
Methods: In this secondary endpoint analysis of the trial, we report on 15 study subjects who have received 3 months of treatment with clazakizumab (n=7; 25 mg s.c. monthly) vs. placebo (n=8). IL-6, IL-6R and gp130 RNA was determined by real-time qPCR (peripheral blood) and microarray analysis (protocol biopsies performed after 12 weeks of treatment). For detection of total IL-6, unbound IL-6, soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R) and serum amyloid P component (SAP) measurement on a protein level, magnetic bead-based immunoassays were used.
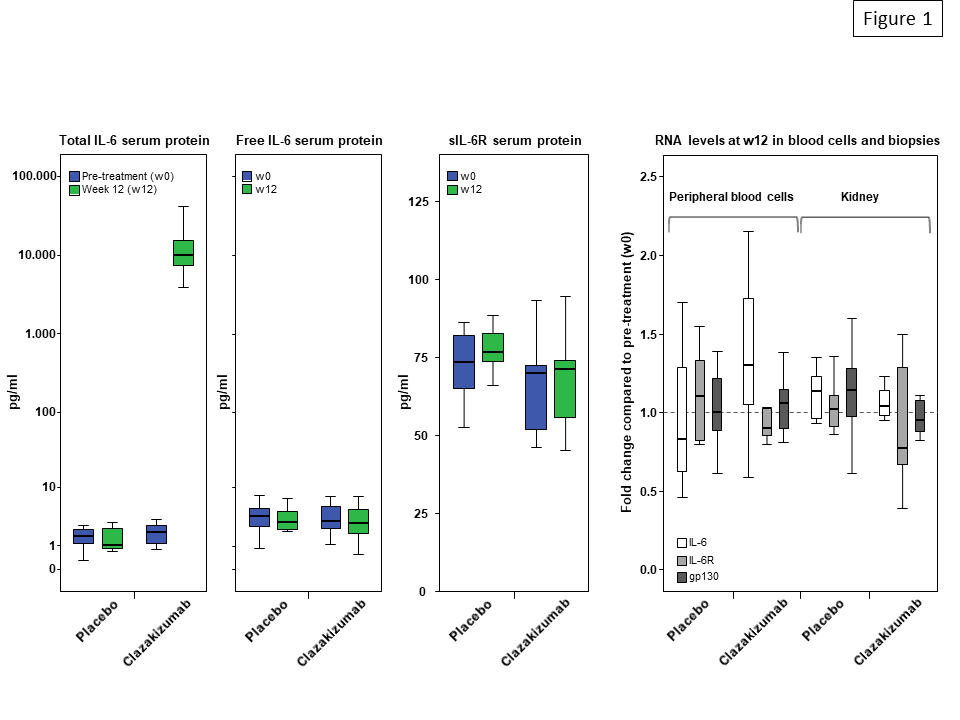
Results: After 12 weeks of clazakizumab treatment, median serum levels of total IL-6 (but not levels of unbound IL-6) increased from 2.0 pg/ml at baseline to 10,050 pg/ml (p=0.001, placebo group: 1.7 pg/ml to 1.1 pg/ml). IL-6 blockade, however, did not result in significant changes of RNA expression of IL-6, IL-6R and gp130, neither in peripheral blood nor in kidney biopsies (Fig. 1). Treatment did not have any impact on serum concentrations of soluble IL-6R. In support of effective anti-inflammatory activity of treatment, serum levels of SAP and CRP were substantially reduced.
Conclusion: Our results may argue against a role of potentially harmful rebound phenomena within the IL-6/IL-6R axis under treatment with the anti-IL-6 antibody clazakizumab.